What is A Human Milk Bank?
When babies are born premature or weighing less than 1,500 grams, they are still physically undeveloped to live outside the womb, which puts them at risk of many illnesses. For these babies, human breast milk is not just nutrition, but also as vital as medicine for protecting them from infectious diseases or intestinal illness.*
In particular, compared to infant formula, breast milk is said to reduce the risk of contracting necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), an often-fatal disease which causes part of the intestines to die, by around two-thirds.
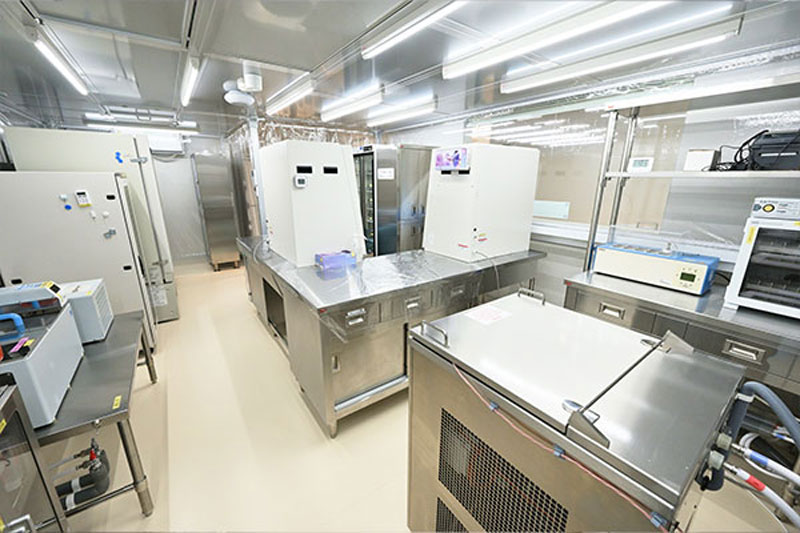
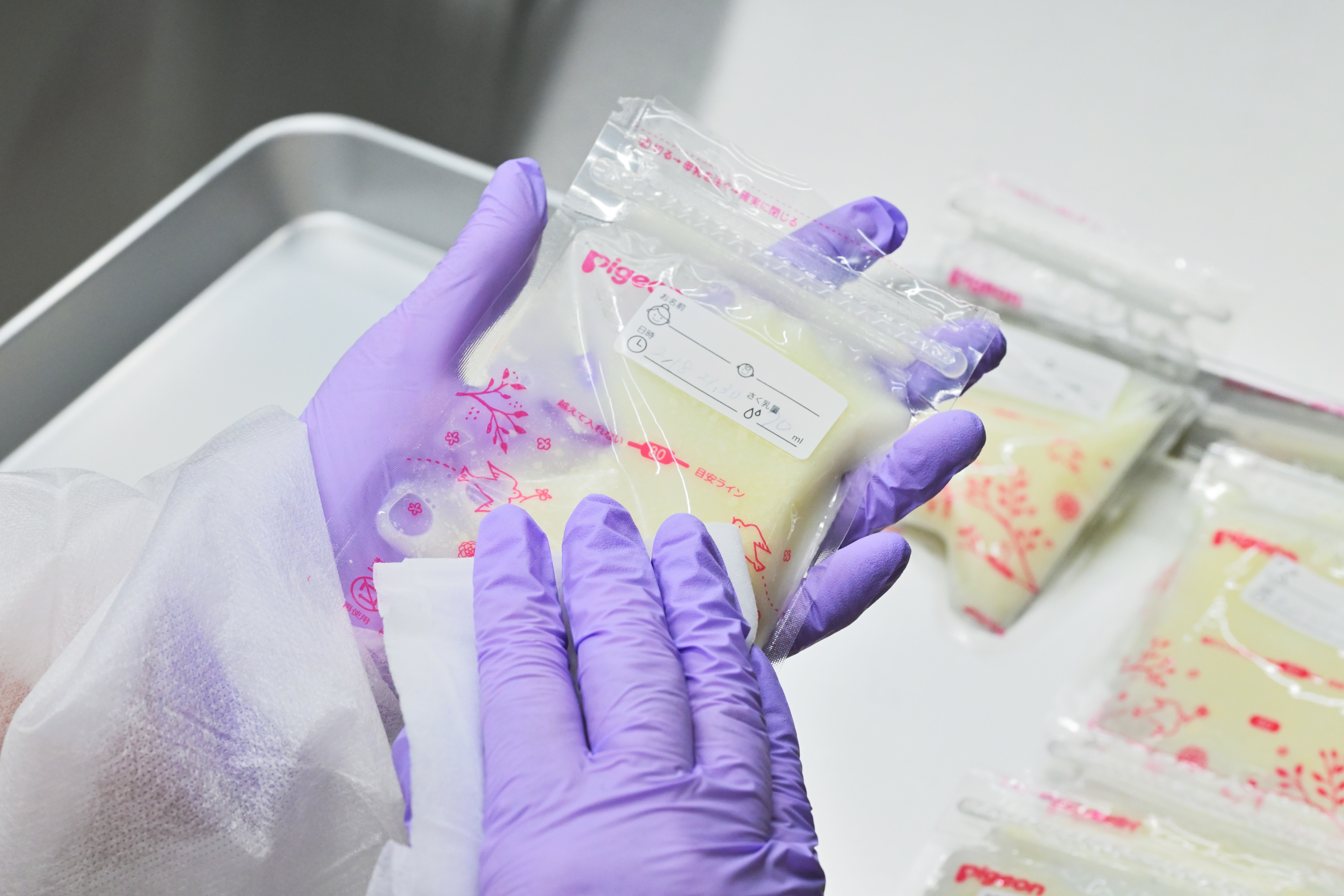
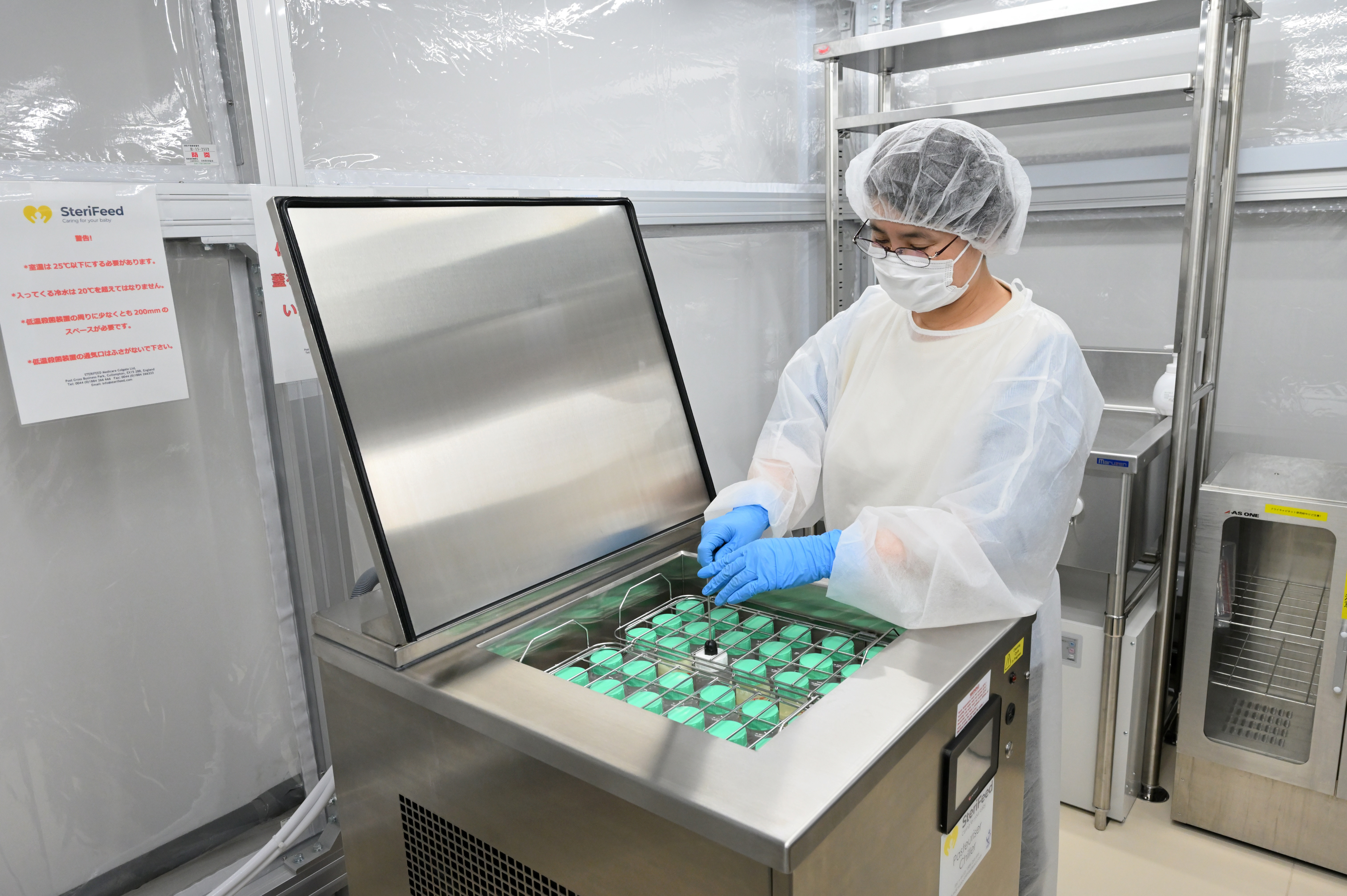
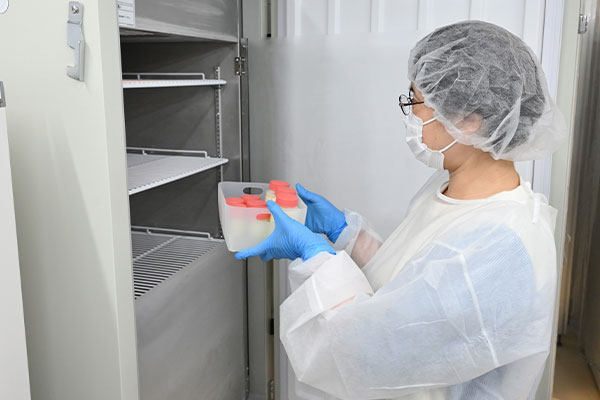
Human milk banks are facilities that accept donated breast milk, pasteurize it at low heat for safety, and provide this donor milk to babies whose own mothers are unable to provide enough breast milk to them due to illness or lactation issues.
* Whether or not to use donor milk is based on a doctor’s assessment.
QUIGLEY M A.HENDERSON G. ANTHONY MY. ET AL.FORMULA MILK VERSUS DONOR BREAST MILK FOR FEEDING PRETERM OR LOW BIRTH WEIGHT INFANTS. COCHRANE DATABASE SYST REV. 2007; (4):CD002971.
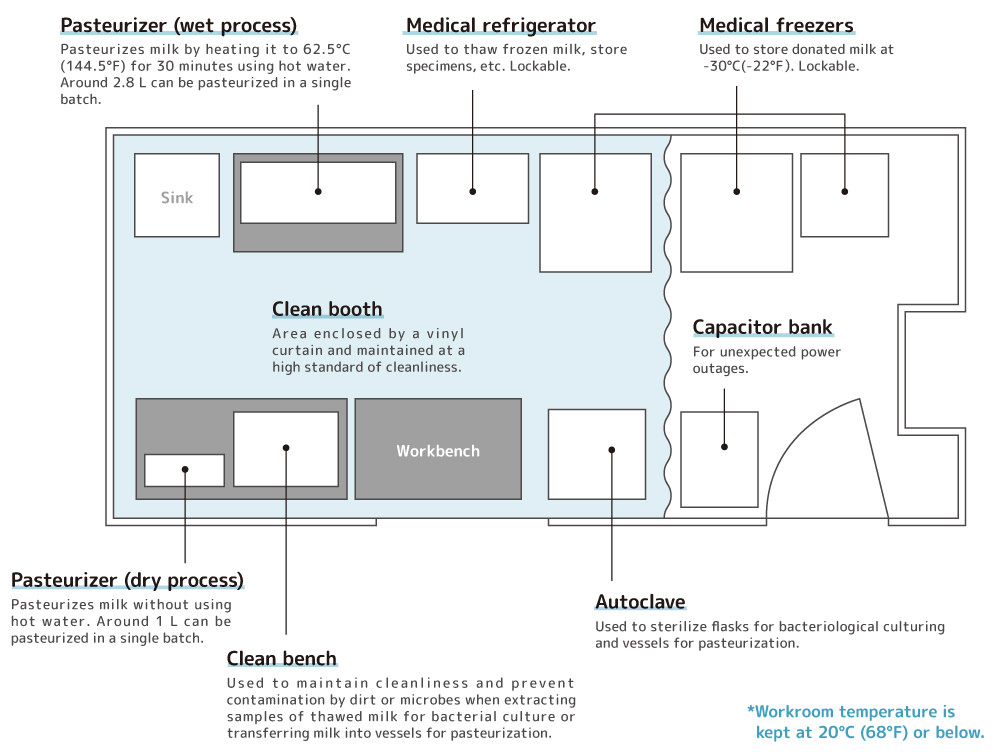
How the Human Milk Bank Works
Q&A
Human Milk Banking FAQs
-
- QWhat kind of babies need donor milk?
- A
As a general rule, in Japan, donor milk is currently provided to babies born weighing less than 1,500 grams ("very low birthweight babies") who cannot obtain milk from their own mothers. Whether or not to use donor milk is based on a doctor’s assessment, but it is used in cases where the baby is at risk of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), a potentially life-threatening disease for newborns.
Note: In the West and other regions, "low birthweight babies" born weighing less than 2,500 grams are the main recipients of donor milk.
-
- QCan anyone who is lactating donate breast milk?
- AMothers who meet the following conditions can apply to become donors.
* Note: In some periods, no donor applications are accepted. See the Japan Human Milk Bank Association homepage for details.
Japan Human Milk Bank Association- Produces sufficient breast milk
- Has no infectious diseases
- Does not smoke
- Is not taking any medicine that affects breast milk
- Has never received a blood transfusion or organ transplant
- Has no medical history of malignant tumors such as leukemia or lymphoma
-
- QWho do I ask for donor milk if I need it?
- ADonor milk is provided only when a baby’s consulting physician determines that it is necessary.
-
- QIn what ways is donor milk superior to infant fomula?
- AInfant fomula is derived from cow’s milk. This makes it harder to digest for very low birthweight babies, whose intestinal lining is still weak.
Compared to babies who drink infant formula, babies who drink human breast milk also have lower rates of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). NEC causes part of the intestine to die, making it potentially life-threatening for very low birthweight and other babies.
-
- QWill donors pump milk in the lactation lounge on the first floor of Pigeon's head office and then give that milk directly to the Nihonbashi Human Milk Bank?
- ANo. As a general rule, donors will pump milk at their homes, freeze it in a freezer bag, and then send it to the human milk bank via frozen courier. Donors will not pump milk on-site to give to the Nihonbashi Human Milk Bank directly.
-
- QHow do I apply to register as a donor?
- ARefer to the Japan Human Milk Bank Association homepage for information.
Japan Human Milk Bank Association













Comment from
Dr. Katsumi Mizuno
Representative Director,
Japanese Human Milk Bank Association
From the mothers who donate milk to human milk banks, to the mothers who see their children nourished by that milk; from the doctors who make the decision to use donor milk to the nursing staff who handle it, countless people are involved in using the donor milk processed at human milk banks. We must answer all of the questions that these people have: Why is donor milk necessary? Is it safe? What do human milk banks do? With the opening of the Nihonbashi Human Milk Bank, we can hope to become familiar to more people than ever. One distinctive feature of human milk banking in Japan is that government, private industry, and academia work together to save the “tiny lives” of our recipients. This is unheard of overseas. As the birthrate falls in Japan, I hope that everyone will offer even more support for activities that help each and every individual baby grow up strong and healthy.
Dr. Katsumi Mizuno
Representative Director, Japan Human Milk Bank Association
Professor, Department of Pediatrics, Showa University
Council Member, Japan Pediatric Society
Request for Assistance The Japan Human Milk Bank Association is soliciting donations from individuals (from 3,000 JPY) and organizations (from 100,000 JPY). If you support the goals of the association, please consider offering assistance in the form of a financial contribution to help more tiny lives grow up strong and healthy. For details, please contact the Japan Human Milk Bank Association.